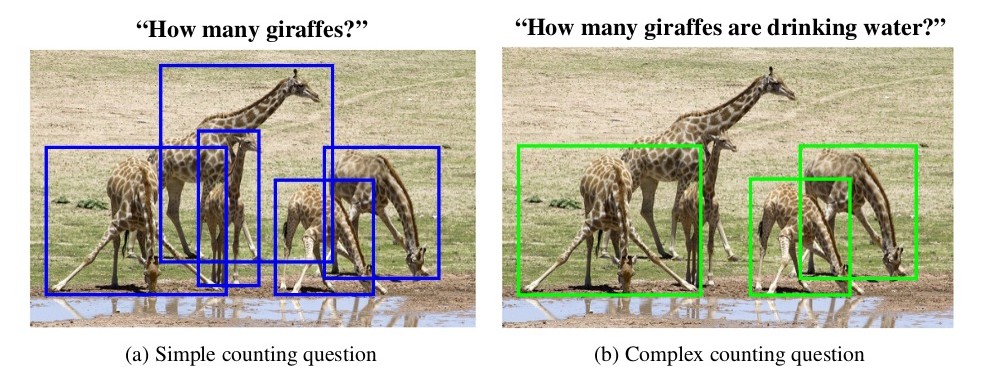
Most counting questions in Visual Question Answering (VQA) datasets (e.g., VQA 1.0 , VQA 2.0, and TDIUC) are simple and can be easily answered using an object detector. Complex counting questions involve understanding relationships between objects along with their attributes and require more reasoning. Thus, performance of counting models cannot be estimated on complex counting questions using these datasets. To address this, we created the TallyQA dataset that has both simple and complex questions. Simple counting questions are those which require only object detection whereas complex counting questions demand more, as shown by the example image below.
Many questions in the previous VQA datasets look complex but easy to answer even using an off-the-shelf object detection system. For e.g., "How many men are wearing glasses?" is not difficult if all of the men in the image are wearing glasses. To ensure that we get quality complex questions, annotators were told to ask questions in which there were counter examples, e.g., to ask "How many men are wearing glasses?" only if it had an answer greater than zero, and the contrary question "How many men are not wearing glasses?" had an answer greater than zero.
The distinction can also be understood by the following examples.

The distinction can also be understood by the following examples.

TallyQA Stats
As of Nov. 2018, TallyQA is the largest open-ended counting dataset for VQA. It is also the only dataset to distinguish between simple and complex counting questions. In summary, it has- 287K questions
- 165K images
- 19K complex questions collected from human annotators using AMT


